Multispectral Drones
Capture precise data beyond what the eye can see
What Is Drone Multispectral Imaging?
Drone multispectral imaging offers valuable insights into the health, condition, and dynamics of the environment, enabling informed decision-making and effective management practices.
Multispectral imaging captures and records light across the electromagnetic spectrum -including outside of the visible spectrum, such as infrared and ultra-violet. It extracts information that the human eye or standard industrial vision cameras fail to capture.
Using a multispectral drone increases survey speed, reaches hard-to-access locations, and enables repeatable data collection to track changes over time.
Multispectral data capture benefits agriculture, forestry, and land management applications.

What Are The Benefits Of Multispectral Data Capture?
Crop Health Monitoring: Detect subtle changes in crop health for early detection of stressors such as pests, diseases, nutrient deficiencies, or water stress. Take timely corrective measures and optimise crop yields.
Precision Agriculture: Spatial variability of crops and soil conditions aids variable rate application of fertilisers, pesticides, and water. Improve resource efficiency, reduce input costs, and minimise environmental impact.
Vegetation Mapping and Analysis: Observe vegetation types, coverage, and health over large areas. Valuable for forestry management, biodiversity assessment, and habitat monitoring.
Environmental Monitoring: Check environmental parameters such as water quality, land cover changes, and ecosystem health. Identify pollution sources, assess habitat suitability, and monitor natural ecosystems.

Multispectral Bands And How They Help
Multispectral imaging captures images in various spectral bands (ranges of wavelengths). These include:
Red (600-700nm): Detect vegetative growth and vigor, crop type, humidity, and generates leaf area index.
Near-infrared (700-900nm): Measure plant health and productivity.
Red-edge (700-780nm): Detect crop stress; can indicate changes in chlorophyll content.
Green (500-600nm): Measure canopy cover and detect weed growth.
Blue (450-500nm): Detect water stress, disease, and large differences in plant health.
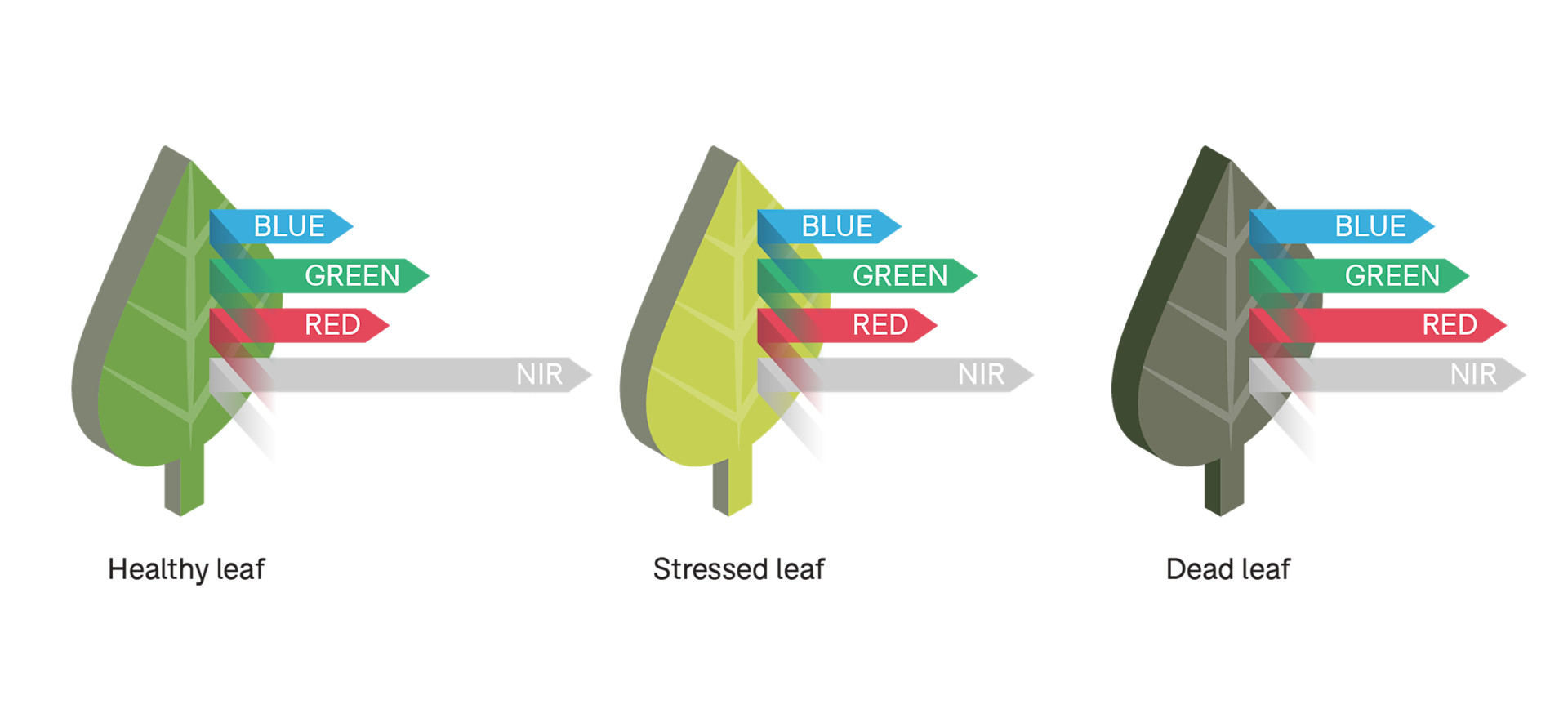
Using Vegetation Index Data
Vegetation indices provide a more in-depth view of vegetation health and productivity. They comprise two or more image bands to enhance analysis of various characteristics of vegetation.
Commonly-used vegetation indices include:
NDVI (Nir-Red)/(Nir+Red): Shows plant vigor; differences in soil water availability; foliar nutrient content (when water is not limiting); yield potential.
NDRE (Nir-RedEdge)/Nir+RedEdge): Shows leaf chlorophyll content; plant vigor; stress detection; fertiliser demand ; nitrogen uptake.
OSAVI (Nir-Red)/(Nir+Red+0.16): Differentiate soil pixels; detect chlorophyll; observe non-linear interactions of light between soil and vegetation.
GNDVI (Nir-Green)/(Nir+Green): Determine water and nitrogen uptake in the crop canopy.

Best Multispectral Drones
DJI Mavic 3 Multispectral: The Mavic 3 Multispectral is all-in-one platform with four 5MP multispectral cameras, 20MP 4/3 RGB sensor, and RTK module for precision surveying. It is small, compact, and foldable for easy transportation/quick deployment. Generate datasets, including multispectral maps, through DJI Terra.

DJI M300 Series: The DJI M300 Series is a flagship drone range with interchangeable payload capability. Integrate these drones with leading third-party multispectral sensors from the likes of MicaSense and SlantRange.

End-to-end Workflows With Multispectral Drones
Use the DJI Mavic 3 Multispectral as part of a precision agriculture workflow. This includes:
1: Orchard Mapping:
Mavic 3M allows terrain-follow aerial surveying of orchards, even on sloped landscapes.
Use DJI Terra to reconstruct high-resolution orchard maps, automatically identify the number of trees, distinguish trees from other obstacles or objects.
Then generate 3D operation routes for agricultural drones, making operations safer and more efficient.

2: Guide Variable Rate Applications:
For rice fertilisation, cotton growth regulation, and potato foliar fertiliser spraying, use Mavic 3 Multispectral to obtain multi-spectral images of crops.
DJI Terra then generates NDVI and other vegetation indices maps, capturing differences in crop potential and generating prescription maps that allow agricultural drones to execute variable-rate application.
This allows users to reduce costs, increase yield, and protect the environment.

3: Intelligent Field Scouting
Mavic 3M can carry out automatic field scouting. The field scout images can be uploaded to the DJI SmartFarm Web in real time through a 4G network.
It can find abnormalities, such as emergence deficiencies, weed pressure, and crop lodging in a timely manner.
Use identification for real-time sharing of crop growth information, guidance of agronomic activities, and easy management of 70 hectares of farmland by one person.
How heliguy™ Supports Your Drone Surveys
In-house geospatial specialists offering consultancy, proof of concept, equipment supply, and drone survey training.
Drone Assistive Programme: Our specialists can attend your site to help you collect real-world data to help you learn on the job.
Obtain your permissions to fly your drone with the support of our 10-strong training team.
Access the UK's largest drone rental fleet to access equipment on-demand, only when you need it.
Leverage support from our in-house DJI-approved repair centre, should something go wrong with your equipment or you crash your drone.